After angiography (done for episodes of anginal chest pains), how do doctors decide whether to go for angioplasty (balloon dilatation of blockages of arteries of heart) or surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting or CABG, often called 'cabbage')? Thanks for your comments and answers.tca
2 Answers
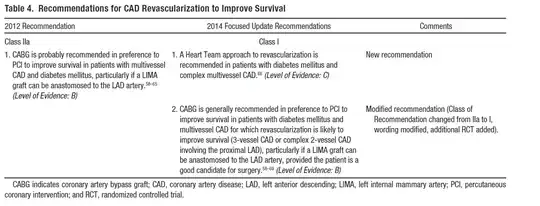
Patients with following features on angiogram have better results with coronary bypass surgery (CABG) than after angioplasty (percutaneous coronary intervetion, including balloon dilatation, stenting etc):
- Left main coronary disease
- Multi-vessel disease in patients with diabetes mellitus
- Triple-vessel disease with left ventricular dysfunction
- Double vessel disease, including proximal left anterior descending artery involvement, and left ventricular dysfunction
- Calcified vessels
- Diffusely diseased vessels
- Highly tortuous vessels
- Ostial lesions
- Bifurcation lesions
These features indicate that angioplasty may be associated with greater likelihood of suboptimal immediate result and/or greater risk of complications later on (such as restenosis or the dreaded subacute thrombosis in the treated artery). Hence, bypass surgery is generally advisable in these cases.
References:
http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/126/25/e354.full
http://sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/96/index.html
http://eurheartj.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2013/08/28/eurheartj.eht296
- 1,770
- 9
- 14
-
what about EECP (Enhanced External Counterpulsation) therapy ? would it help some ways to avoid either of these commonly advised methods ? – Sooraj S Feb 22 '16 at 19:02
There have MANY trials comparing PCI (intervention during the "cardiac cath" procedure) which are well referenced in this guideline update. (Note, the "Heart Team" approach mentioned below relies on the combination of the expert opinion of the interventional cardiologist was well as the cardiac surgeon.)